select disk 0
dir
And hence, I went out to ‘fix this non-issue’ and I am going to share how you can do the same if you like.
exit
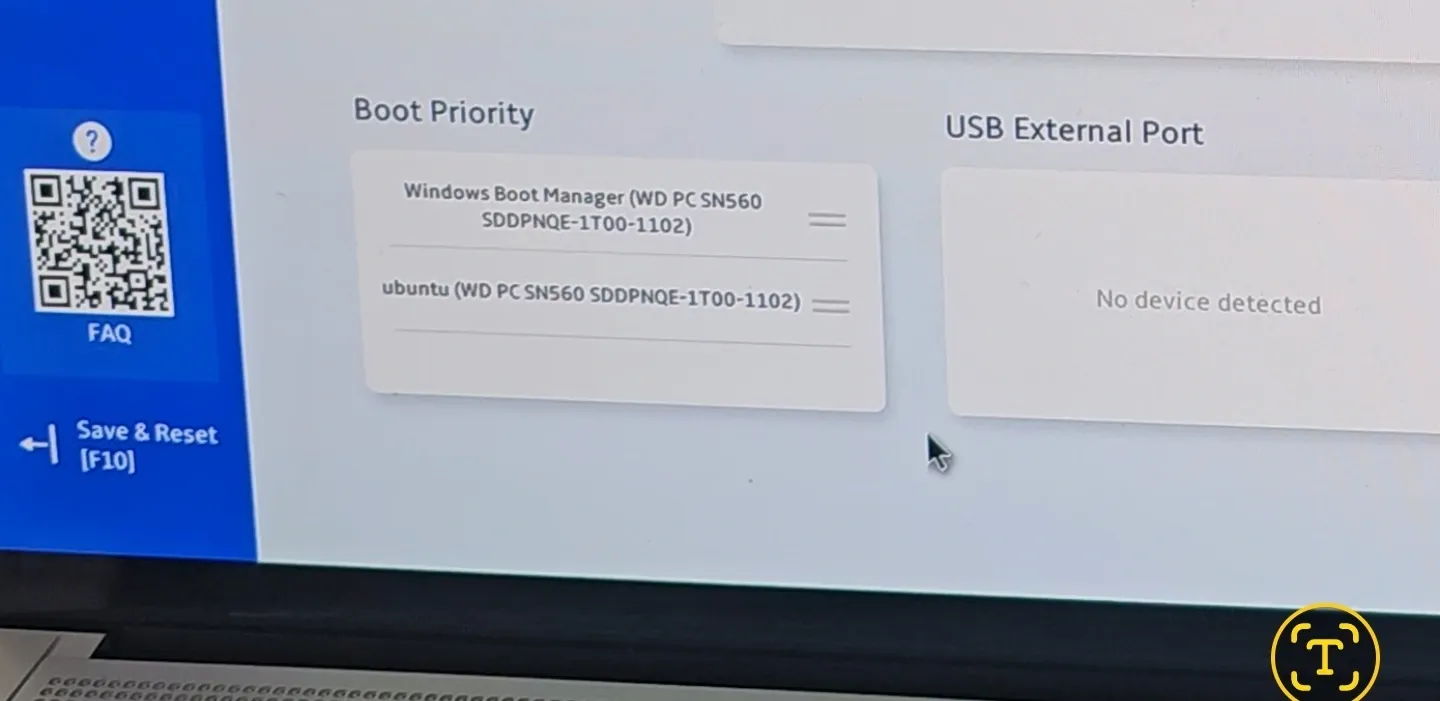
Step 2: Delete Linux folder from EFI
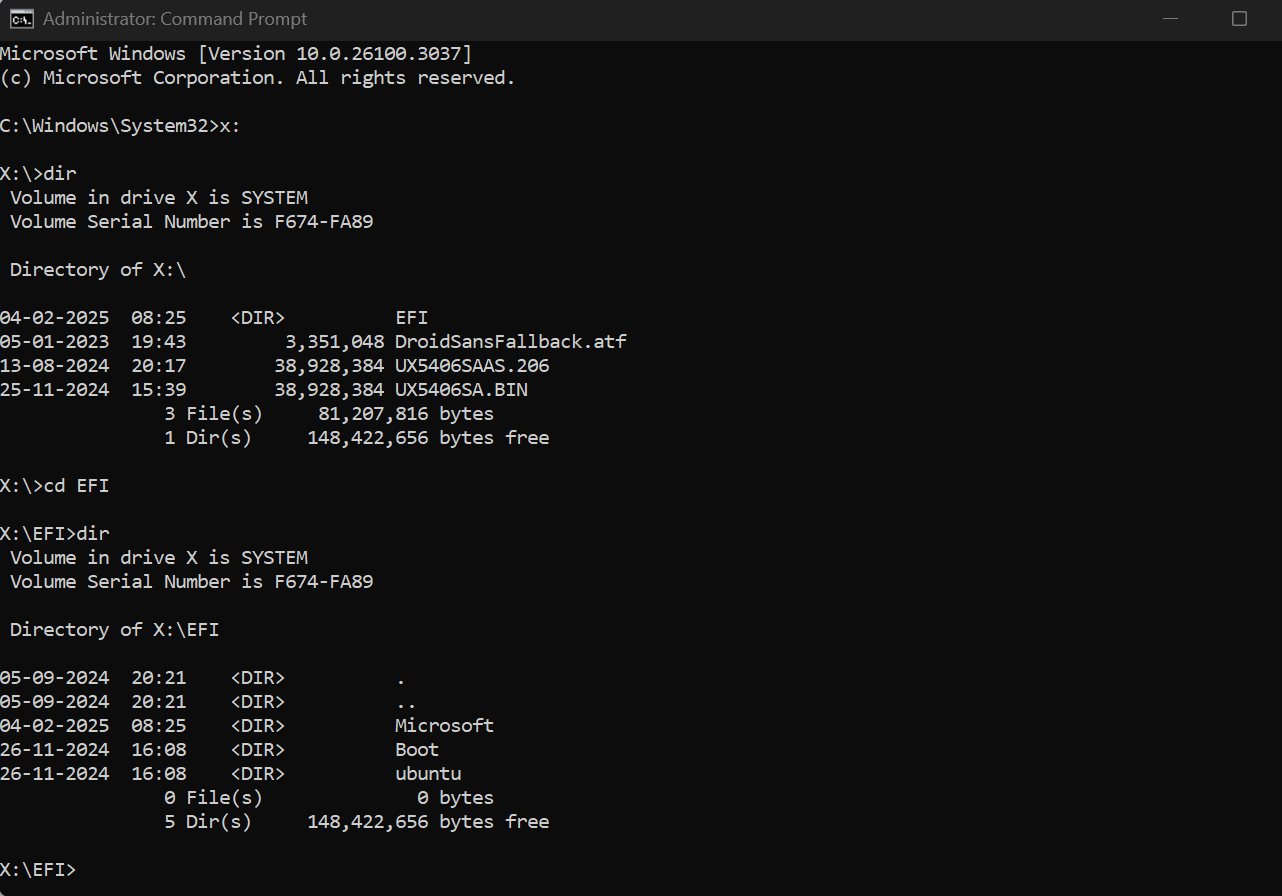
Since my ESP (EFI System Partition) has assigned number 1, I’ll select this partition. Yours could be different, so pay attention.x:
Browse to drive X and the EFI folder. You should see ubuntu (or whichever distro you used) listed here. Select it first and then right click to see the option to delete it. Browse to drive X and the EFI folder. You should see ubuntu (or whichever distro you used) listed here. Select it first and then right click to see the option to delete it. Once the command prompt is open, start the disk partition utility by entering:
💬 Is it worth the hassle to clean up the Linux boot entry after removing it from dual boot? Share it in the comments, please.You can now browse the partitions and the files inside them. Using this, you can add or delete files and folders.Command line warrior? Let’s see the other method for you.list partition
Now, list all the partitions on this disk with:
This is typically done by moving the Windows boot manager up the boot order and deleting the Linux partition from within Windows.The annoyance is that Linux will still show up in the UEFI boot settings.
Conclusion
In a YouTube video, I discussed uninstalling Ubuntu from the dual boot system, I mentioned the fact that a leftover Ubuntu entry in the boot doesn’t hurt. Still, a few comments indicated that they would like everything cleaned up. Hence, this tutorial.Basically, all this hassle for mounting the ESP partition. Anyway, exit the disk partition tool:diskpart
Type “list disk” to list all the disks present on your system and get the name of the disk where the EFI partition is located.