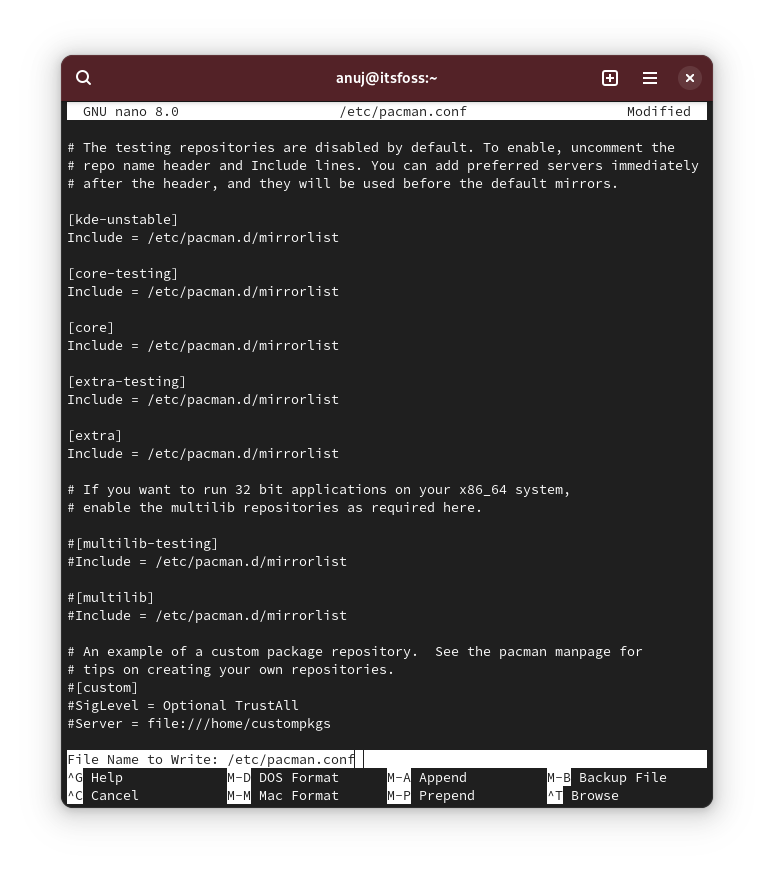
To enable the above two desktop specific repos you have to add two lines unlike all the above repos where you just uncomment the lines. Below is the screenshot which shows the configuration with kde-unstable enabled.To disable the multilib repo, you have to comment out (means add “#” without quotes) before the two lines corresponding to the multilib repo and then update your system using below command:To disable any of the testing repo you can simply remove them from the config file or comment them out by adding “#” without quotes.Secondly, the desktop repo should be mentioned before all the repos in the configuration at the top similar to the config above.
Enter the below command to edit the configuration file using nano or a terminal-based text editor of your choice:
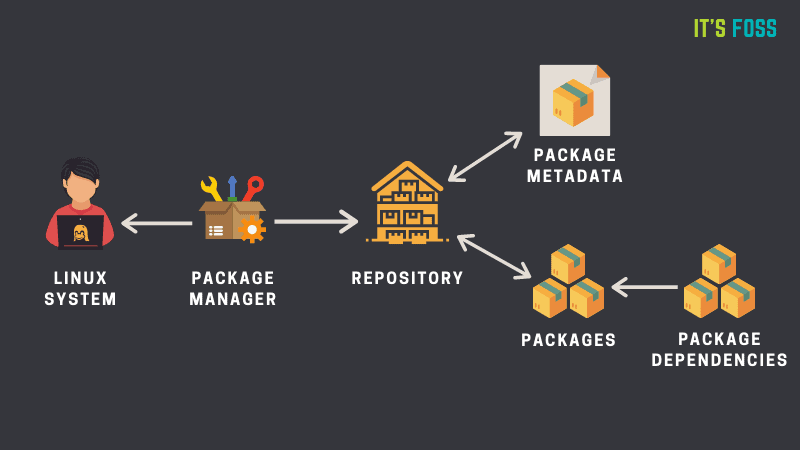
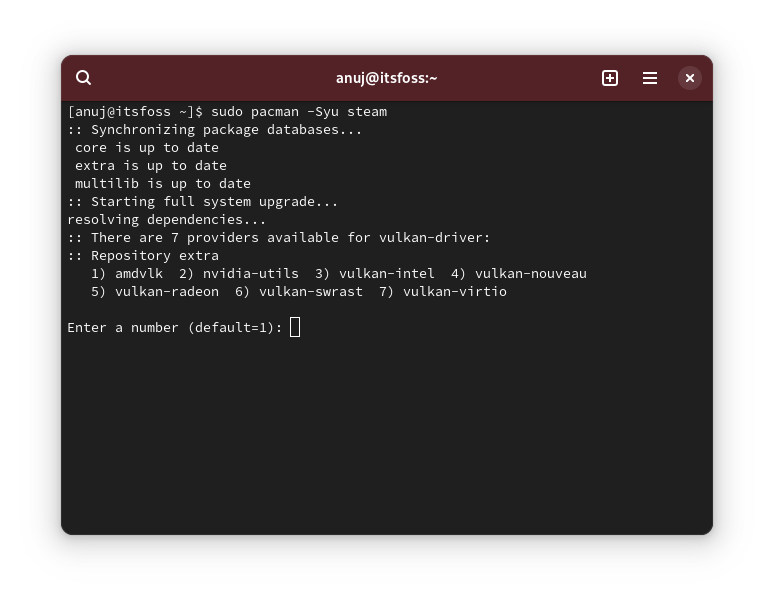
sudo pacman -Syu
Save the file and update the system so that it knows about the packages from the newly added repos:
Table of Contents
Core
Yes, you guessed it right. This repo is the counterpart to multilib repo containing the latest version of the packages.I will advise you to stay away from all the testing repos if you don’t know what you are doing. It is not worth the hassle to install the latest kernel or the flashy new KDE version from testing repos.One of the use cases is to enable this repo could be that you have very recent hardware and only the latest kernel will suffice. However, it does not take more than two weeks for the kernel to be in stable repos. You’ll have to update the system after making any changes to the repository configuration.This repo is generally empty when a Gnome version has released recently and is available in stable repos already. It fills up only when Alpha build of the next Gnome version is available upstream.
Multilib
sudo nano /etc/pacman.conf
This repo is meant to test the prerelease versions of the Gnome desktop environment when available upstream. It should be enabled only if you want to test out the latest versions of Gnome before they are released in the stable repos. After your system is updated you can remove the packages installed from the repo by using the command below. However, this command will remove all the packages installed that are not present in core and extra repos e.g. AUR packages.If you looked at the configuration carefully, you will notice that all the testing repos are enabled and the kde-unstable is mentioned before all the repos. This implies that if you want to enable the desktop specific repos, testing repos should also be enabled first. This repo is the counterpart to the core repo as its name suggests and to enable this repo, you need to uncomment the repo similar to the multilib repo mentioned above.
This is the second arch repo which is enabled by default and does not need user configuration similar to the core repo. It basically contains the packages for Desktop Environments, Applications, etc. Below is the screenshot of the /etc/pacman.conf file with all the testing repos enabled along with multilib repo. Your configuration file should look like the one shown below.
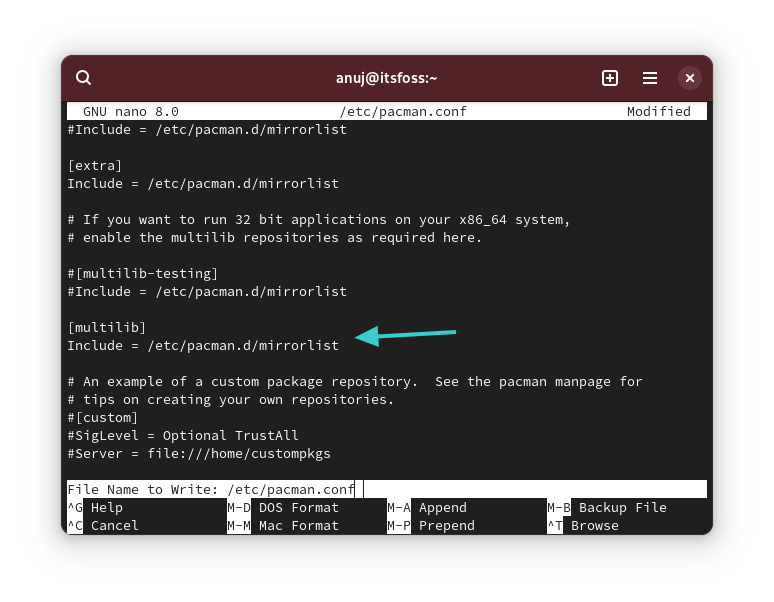
This repo should be enabled only if you have multilib repo already enabled. Otherwise keep it disabled.To enable it, you need to edit the configuration file of pacman located at /etc/pacman.conf. It is enabled by default and thus it does not need user input or configuration.
You should not enable these repos for the sake of getting the latest versions of the packages. Only some advanced users use them to test out new software versions.The official Arch repos can be classified into Stable and Testing categories. Let’s go through them.
Core-testing
But there is one caveat if you want to enable these repos. Both of these repos have to be enabled simultaneously. Your system can break if you enable only one of them.As the name suggests, these repositories contain the packages safest to install and you can easily rely on the packages in these repos.Another thing to notice in the above config is that the Multilib repo is disabled here.I hope this article helped you get familiar with the arch repos. The gist of this article is that if you want to install Steam or Wine in Arch Linux, you have to enable the multilib repo.
Multilib-testing
One of the most popular unofficial arch repo (IMHO) and which I can suggest is Chaotic-aur maintained by Garuda Linux team. I am telling you from my experience that sometimes Pacman refuses to revert back to stable packages, which gets pretty frustrating. However, a VM will come in handy if you just want to get rid of the itch to experience and test the latest/greatest software packages.pacman -Qqm | sudo pacman -Rns -
Testing repositories
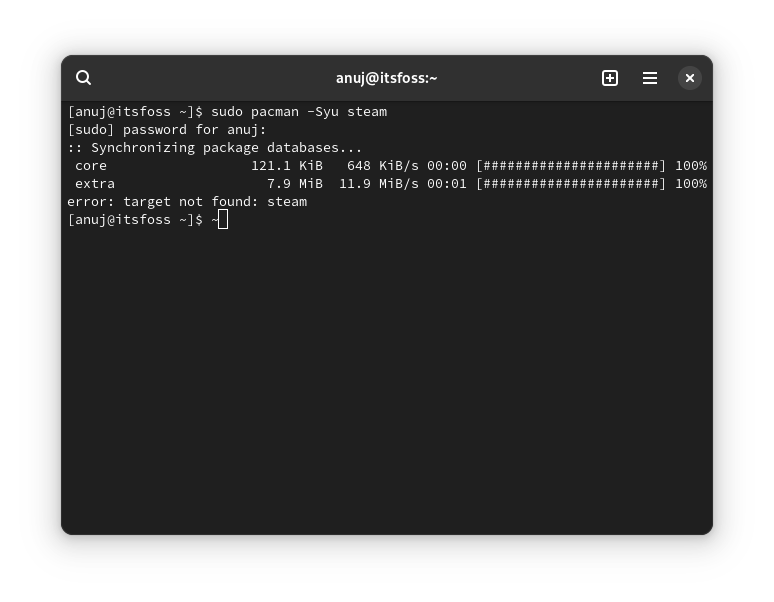
The multilib repo basically contains packages for Steam and Wine. If you want to install Steam or Wine on Arch, you need to enable this repo.
Gnome-unstable
But, the question arises: why bother about these repos in the first place? Let me give you an example. If you try to install Steam on a fresh Arch Linux install, you are likely to encounter the error ‘target not found: steam’.🚧
Kde-unstable
You will notice it contains exponentially more packages then the core repo. It contains packages that are not essential for a base system and packages in the repo are not stringently tested as compared to the core repo.This is one of the main arch repos containing the essential packages for a working system.
I have already mentioned this in one of my previous articles about installing Pamac in Arch.You can also check out archwiki for more interesting unofficial repos. But make sure that you trust the host of the repo and that the packages are signed.After saving the configuration file, update your system and you will be on the testing repos.This is the last of the arch stable repos and contains only 32 bit packages. This is the only stable repo that is not enabled by default. This repo is the counterpart to the extra repo, as the name meant indeed. It has the same purpose as all of the testing repos, i.e., to test the latest versions of packages that need some testing to be used in production or to be transferred to stable repos.
Bonus (unofficial repositories)
sudo pacman -Syu
pacman -Sl multilib command. 32-bit library package names begin with lib32-.
The bottom line
You’ll find these terms ‘strange’ when you are just starting your Arch journey but you’ll come across them in various forum discussion and wiki references.Hence, I thought of writing this tutorial to quickly explain the different kinds of repos Arch Linux offers and how you can enable them.You’ll learn why you see the above error in a moment. Before you read further, I advise a quick go through the article below.