
You should note that nvme0 should be used as /dev/nvme0. If the /dev is omitted, nvme-cli won’t show output, and results in a syntax error.sudo apt install nvme-cli
The nvme0 is the top-level device file. The nvme0n1, nvme0n2, etc. are name spaces. Since temperature is a physical property of the drive, to check the temperature of a drive, you can use the top-level device file.On the panel, click on the temperature option to expand the temperature monitors. From there, you can monitor the NVMe temperature in real time.In this quick tutorial, I will use this tool to measure the temperature of NVMe SSDs.If you are using Ubuntu or any other Debian-based Linux distribution, nvme-cli is available in the official repositories. To install, just run:
Table of Contents
Install nvme-cli
The syntax used to check the temperature is:On a similar note, you may want to know a thing or two about checking CPU temperature on your Linux system.
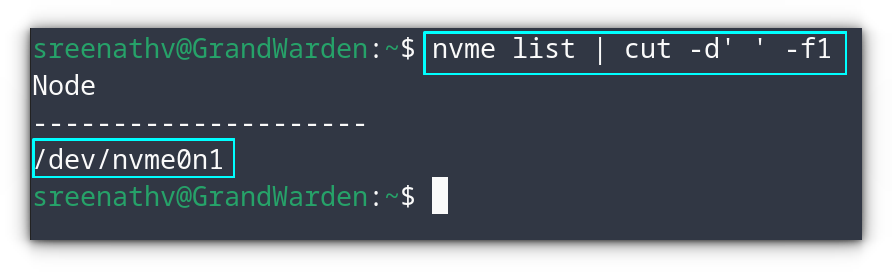
Listing the NVMe drives in the system
As you can see, we got the name of the NVMe device. Also, you can use the lsblk command to list all the drives attached and then find the name of NVMe from there.If you are a GNOME user, Vitals is a must extension. It is not limited to temperature, instead it offers a whole lot of other system monitors.While nvme-cli is the comprehensive tool to check the temperature, a few alternative solutions offer a more convenient GUI. Let’s see them.
In order to check the temperature, you need the NVMe device name. This is not the manufacturing name, instead the NVMe block device location on Linux.Hardinfo2 is a system information and benchmark tool. You can use this to know the temperature of your devices.The nvme-cli is a simple tool that lets you control and manage your NVMe SSD drive right-from the terminal. It gives you more control over its performance and behavior.
Checking the temperature of SSDs
Now you know the name of the drive you want to check, let’s check the temperature.sudo nvme smart-log /dev/nvme0 | grep -i '^temperature'
nvme command.sudo nvme smart-log <device-name> | grep -i '^temperature'
lsblk | grep "nvme"

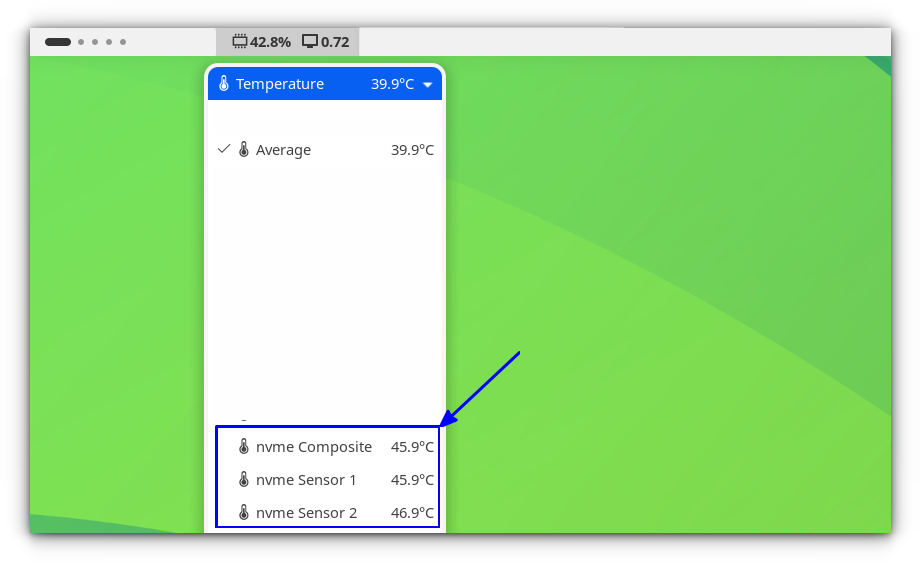
Hardinfo2
Like all other functional devices, NVMe devices also heat upon usage. If they heat too much, it will degrade the performance of your system.nvme list | cut -d' ' -f1
Recently, NVMe, short for Non-Volatile Memory Express drives, has become the go-to storage option for modern desktops. Unlike traditional hard drives, NVMe drives are significantly faster, allowing for quicker boot times, faster file transfers, and smoother overall performance.You can go to the sensors page under the Devices section for the purpose.
The nvmi-cli tool is an awesome tool for your NVMe SSDs on Linux. I prefer it for its simplicity. Not everyone would be comfortable with a CLI tool and hence I added a couple of GUI options.







